LASIK eye surgery stands as the most trusted solution for vision correction today, with over 18 million procedures performed worldwide. This precise 20-minute procedure helps 85% of patients achieve vision correction within ±0.5 diopters of their target prescription.
Your eye doctor may recommend different surgical options based on your specific vision needs. While LASIK works well for many patients, other procedures like PRK might be more suitable if you have thin corneas. For patients with extreme refractive errors, implantable lenses often provide better results.
Talk with your eye doctor about whether surgery is right for you. Most eye doctors suggest considering vision correction surgery when your refractive errors – nearsightedness, farsightedness, astigmatism, or age-related vision changes – begin to affect your quality of life or interfere with daily activities.
This guide examines the most effective surgical procedures available today, their success rates, and key factors that help determine which option suits your vision needs best. Understanding these choices helps you make an informed decision about your eye care, working closely with your doctor to achieve the clearest possible vision.
Understanding Refractive Errors in Eyes
Our natural lens is like a camera lens – crystal clear in most of us. When the eye’s shape becomes abnormal, light can’t focus correctly on the retina, causing blurred vision. These vision problems affect millions globally, making them the most frequent eye disorders in the United States.
Common vision problems that need surgery
Your eye doctor may diagnose one of four primary types of refractive errors that often require surgical intervention:
Nearsightedness (Myopia): This condition typically develops between ages 6 and 14, making distant objects appear blurry. Children who spend more time outdoors during these years show lower risk of developing myopia. Severe nearsightedness increases the risk of retinal detachment.
Farsightedness (Hyperopia): Most people are born with this condition, which makes nearby objects appear blurry. The eyeball is too short, or problems exist with the cornea or lens shape.
Astigmatism: Unlike other vision problems, astigmatism affects vision at all distances. The cornea or lens has an irregular shape, similar to a football rather than a basketball, causing light to bend differently as it enters the eye. Many people with astigmatism also experience nearsightedness or farsightedness.
Presbyopia: After age 45, many people develop this condition that makes focusing on close objects difficult. The eye’s lens becomes harder and less flexible over time, like a camera that can’t adjust its focus.
How refractive errors affect daily life
The World Health Organization reports that 123.7 million people worldwide struggle with visual impairments due to uncorrected refractive errors. These vision problems create significant challenges in daily activities:
- Reading becomes difficult at various distances, particularly affecting children’s academic performance
- Driving becomes challenging, especially at night or when reading road signs
- Workplace tasks become limited, reducing productivity
- Social interactions decrease, particularly among older adults
- Self-care becomes complicated, like distinguishing between personal care products
- Moving around safely becomes difficult, especially on stairs or in dim light
The economic impact proves substantial, with annual global productivity losses reaching USINR 20588.83 billion for uncorrected myopia and USINR 2143.26 billion for presbyopia. People with high myopia (−6 diopters or more) face 22 times higher risk of visual impairment compared to those with normal vision.
Take time to consider your vision correction options with your eye doctor. While glasses remain the most common solution worldwide, surgical procedures offer permanent vision correction for many patients. Your doctor will help determine the best correction method based on your specific refractive error, age, and overall eye health.
LASIK Eye Surgery: The Popular Choice
LASIK eye surgery stands as one of the most frequently performed laser refractive procedures worldwide, with more than 600,000 surgeries completed annually. During this 30-minute procedure, your eye doctor uses advanced laser technology to reshape your cornea for clearer vision.
What happens during LASIK
To ensure your comfort, your eye doctor begins by numbing the area around your eye with special drops. A small device holds your eyelids open while another creates gentle suction to keep your eye steady. The critical first step involves creating a thin corneal flap, which your doctor folds back like turning a page in a book.
The way smudgy lenses cause blurring of vision, your cornea’s shape affects how clearly you see. Your doctor uses a programmed laser to precisely reshape your cornea. This laser tracks your eye position 500 times per second, automatically stopping if needed. During the procedure, you might notice a clicking sound and a distinct odor from the chemical reaction – not from burning tissue.
Finally, your doctor carefully repositions the corneal flap, which begins healing immediately without stitches.
Recovery and results
After the procedure, you’ll notice improved vision within 24 hours. Complete healing and vision stabilization typically takes 2-3 months. During recovery, you might experience:
- Mild discomfort or burning sensation for about five hours
- Some blurred vision that improves within the first week
- Temporary light sensitivity that resolves with proper healing
Talk with your eye doctor about what to expect. More than 8 out of 10 patients no longer need glasses or contact lenses for most activities. Studies show that 98.5% of patients report achieving their main vision goals.
Who can get LASIK
To determine whether LASIK is right for you, your doctor will evaluate several factors:
Age Requirements: You should be at least 18 years old, though preferably in your early to mid-20s when vision typically stabilizes.
Vision Stability: Your prescription should remain unchanged for at least 12 months.
Prescription Range: LASIK effectively corrects:
- Nearsightedness: 0.50 to -12.00 diopters
- Farsightedness: +0.50 to +6.00 diopters
- Astigmatism: +/- 0.50 to +/- 6.00 diopters
Health Considerations: For the best surgical outcomes, you should:
- Have healthy corneas with sufficient thickness
- Be free from severe dry eye syndrome
- Not be pregnant or nursing
- Have good overall eye health
People with mild nearsightedness generally see the most successful outcomes. If you have severe refractive errors or certain health conditions, your doctor might recommend exploring other vision correction options.
Alternative Laser Eye Surgery Options
For some people, other eye problems prohibit the use of traditional LASIK surgery. Your eye doctor might recommend alternative laser procedures based on your specific vision needs and eye health.
PRK surgery process
PRK (Photorefractive keratectomy) was the first significant breakthrough in laser eye surgery. Unlike LASIK, your doctor removes the entire epithelium—the thin outermost layer of the cornea—before reshaping the underlying tissue.
During PRK surgery, your eye doctor:
- Applies numbing drops to ensure your comfort
- Gently removes the corneal epithelium
- Uses a cool excimer laser to precisely reshape your cornea
- Places a protective soft contact lens bandage
After the procedure, you’ll have some discomfort for a few days while your epithelium heals, typically taking 3-5 days. Patient experiences vary:
- One-third report minimal discomfort
- One-third experience mild pain
- One-third face more significant discomfort
Your vision typically stabilizes within 2-6 weeks. Talk with your eye doctor about PRK if you have:
- Thin or flat corneas
- An active lifestyle with risk of eye injury
- A profession requiring enhanced corneal stability
SMILE procedure benefits
SMILE (Small Incision Lenticule Extraction), approved by the FDA in 2016, offers a different approach to vision correction. The way smudgy lenses causes blurring of vision, SMILE corrects your vision through a tiny 2-3 millimeter incision—much smaller than LASIK’s 20mm flap or PRK’s 8mm surface removal.
The success rates speak for themselves:
- Almost all patients achieve 20/40 vision without glasses
- 88% reach 20/20 vision or better
During this 20-minute procedure, your doctor uses precise computer guidance to treat nearsightedness and astigmatism. A femtosecond laser creates a small disk between your corneal layers, which your doctor removes to reshape the cornea.
We see several key benefits with SMILE:
- Lower risk of dry eye problems
- Better corneal stability after surgery
- Quicker recovery than PRK
- Fewer post-surgery complications
Most patients notice clearer vision within 24 hours. For people with higher degrees of nearsightedness who can’t have LASIK, SMILE often provides an excellent alternative. Athletes and active individuals particularly benefit from the small incision approach.
Non-Laser Refractive Surgery Types
Talk with your eye doctor about non-laser vision correction options if laser procedures aren’t suitable for your eyes. These advanced surgical alternatives help people with extreme refractive errors or specific eye conditions achieve clearer vision.
Implantable contact lenses
The way our natural lens helps focus light, Implantable Collamer Lens (ICL) surgery places a special biocompatible lens between your iris and natural lens to correct vision without removing corneal tissue. This 15-minute procedure effectively treats nearsightedness and astigmatism, with nearly 95% of patients reporting high satisfaction.
Your eye doctor will check if you meet these requirements:
- Age between 21-45 years
- Moderate to severe nearsightedness
- Little or no astigmatism
- Good overall eye health
- Stable vision prescription for 6-12 months
ICL surgery offers several benefits:
- Can be reversed if needed
- Lower risk of dry eyes
- Better vision quality than laser surgery
- Works for higher prescriptions (-3.0 to -20.00 diopters)
Refractive lens exchange
During refractive lens exchange (RLE), your eye doctor removes your natural lens and replaces it with an intraocular lens. We often recommend this procedure if you’re over 40 and experience:
- Severe nearsightedness or farsightedness
- Age-related vision problems
- Early signs of cataracts
The 15-30 minute procedure helps about 80% of patients reduce their dependence on glasses. Since the artificial lens doesn’t cloud over time like a natural lens, you won’t develop cataracts in the future.
Intacs and corneal implants
For some people, small crescent-shaped implants called Intacs offer another path to better vision. These tiny devices made of polymethyl methacrylate reshape your cornea’s curve when placed in the corneal stroma.
You might be a good candidate if you:
- Have corneal thickness of at least 450 microns
- See poorly even with glasses
- Have stable vision problems
- Are 21 or older
The 30-minute procedure uses numbing eye drops for comfort. Like ICL surgery, Intacs can be removed if needed, and they improve vision without removing corneal tissue.
Consider the specific aspects of each option. ICL surgery costs approximately INR 337,521.80 per eye, while RLE patients typically need 3-4 days for initial recovery. Most Intacs patients return to normal activities within days after surgery.
These surgical options show excellent success rates for patients who can’t have laser procedures. Your eye doctor will help determine which option suits your vision needs best, considering your age, prescription strength, and eye health.
Choosing the Right Eye Surgery
Talk with your eye doctor about whether surgery is right for you. A thorough eye examination helps determine which procedure might work best for your vision needs.
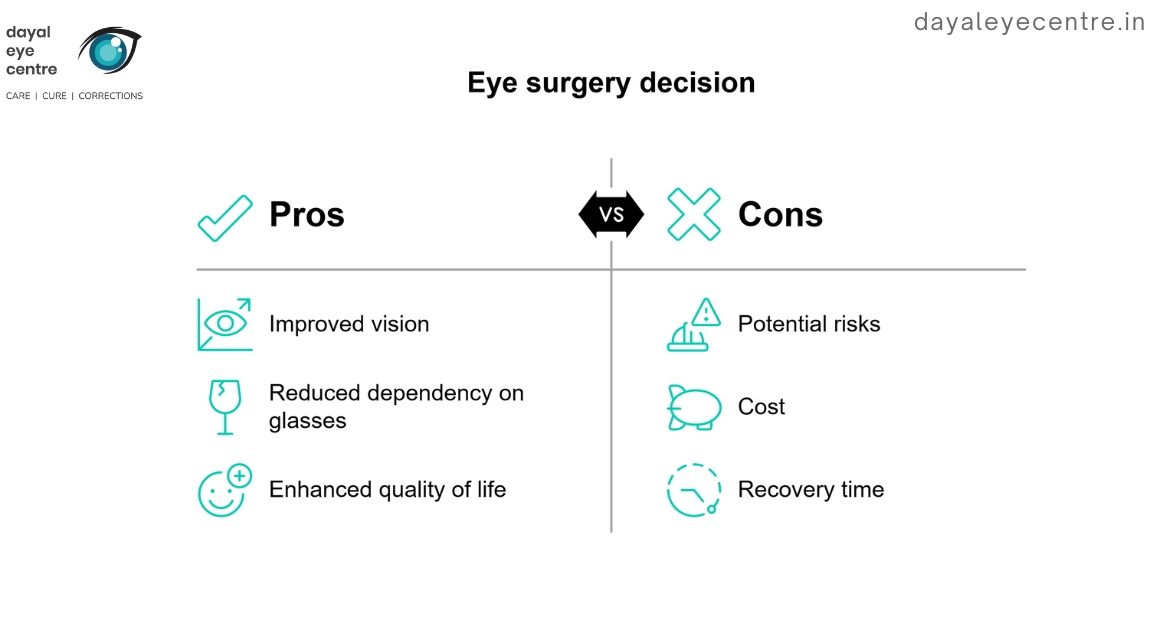
Factors to consider
A comprehensive dilated eye examination reveals whether you’re a suitable candidate for specific procedures. Several health factors affect surgical outcomes:
Medical History: Autoimmune disorders, uncontrolled diabetes, or medications that suppress immune function can slow healing or cause complications.
Eye Conditions: Pre-existing conditions like keratoconus, inflammation, or eye injuries need special consideration. Even if keratoconus runs in your family without personal diagnosis, exercise caution with elective eye surgery.
Age and Vision Stability: Vision should remain unchanged for at least 12 months before surgery. Patients under 18 years might need to wait until their vision stabilizes.
Questions to ask your doctor
To determine whether surgery is right for you, ask your eye doctor:
About Their Experience:
- Number of procedures performed
- Board certification status
- Success rates with cases similar to yours
- Enhancement procedure policies
About Technology:
- Type of laser technology used
- Available surgical options
- Pre-operative evaluation process
About Costs:
- Itemized cost breakdown
- Insurance coverage possibilities
- Additional fees for follow-up care
- Enhancement surgery costs
Cost comparison
The way smudgy lenses causes blurring of vision, different factors affect surgery costs:
Location Matters: Metropolitan areas typically charge higher fees than smaller cities. Surgical costs in major cities reflect advanced facilities and experienced staff.
Technology Choices: Advanced technologies, like femtosecond lasers, increase overall costs. These innovations often provide superior precision and outcomes.
Surgeon Experience: Highly experienced surgeons with successful track records usually command higher fees. This investment often translates to better surgical outcomes and reduced complications.
After-Surgery Care: Consider these additional expenses:
- Follow-up appointments
- Post-operative medications
- Potential complications management
Many clinics offer financing through installment plans or EMIs. Health Savings Accounts (HSA) can contribute up to INR 307,988.65 (2022) in tax-exempt funds toward surgery.
For perspective, traditional vision correction adds up over time. Contact lens users spend approximately INR 1,000 to 4,000 monthly, plus solution costs of INR 100-200. Eyeglasses range from INR 499 to 13,000 every two years.
Take time to consider the benefits and risks of eye surgery with your doctor. A reputable surgeon will thoroughly discuss your options, ensuring you make an informed decision aligned with your vision needs and lifestyle requirements.
Conclusion
Our natural lens is like a camera lens – crystal clear in most of us. Modern eye surgery helps restore this clarity through different procedures, each suited for specific vision needs. While LASIK remains popular for its quick recovery and high success rates, other options like PRK, SMILE, and implantable lenses work better for some patients.
For some people, other eye problems prohibit the use of LASIK. Talk with your eye doctor about which procedure might work best for you. Most eye doctors suggest considering vision correction surgery when your vision problems begin to affect your quality of life or interfere with your ability to perform normal daily activities.
Take time to consider the benefits and risks of eye surgery. Though costs vary based on location and technology, the long-term benefits often outweigh years of spending on glasses and contact lenses. Schedule a consultation with our eye specialists to determine which procedure aligns best with your vision needs.
After the procedure, you’ll notice significant improvement in your vision. The right surgery, performed by an experienced doctor, helps most patients achieve their desired vision goals. Your eye doctor will guide you through the process, ensuring you make an informed decision about your vision care.
FAQs
1. What are the main types of eye surgery for correcting refractive errors?
The primary types of eye surgery for refractive errors include LASIK, PRK (Photorefractive Keratectomy), SMILE (Small Incision Lenticule Extraction), and non-laser options like implantable contact lenses and refractive lens exchange. Each procedure has unique benefits and is suited for different vision problems and patient profiles.
2. How does LASIK compare to other refractive surgeries in terms of recovery and results?
LASIK typically offers quicker recovery and vision improvement compared to other procedures. Most patients experience improved vision within 24 hours, with complete stabilization in 2-3 months. Over 80% of LASIK patients no longer need glasses or contacts for most activities, making it a popular choice for vision correction.
3. Who is an ideal candidate for LASIK eye surgery?
Ideal LASIK candidates are at least 18 years old (preferably in their early to mid-20s), have a stable vision prescription for at least 12 months, and fall within specific prescription ranges for myopia, hyperopia, and astigmatism. They should also have healthy corneas, be free from severe dry eye syndrome, and have good overall eye health.
4. What are the advantages of SMILE surgery over traditional LASIK?
SMILE surgery offers several benefits, including a reduced risk of dry eye syndrome, enhanced corneal stability post-surgery, and faster recovery compared to some other procedures. It's particularly beneficial for individuals with higher degrees of nearsightedness and those leading active lifestyles, as it involves a smaller incision than LASIK.
5. How do I choose the right eye surgery for my vision needs?
Choosing the right eye surgery involves considering factors such as your age, prescription strength, corneal health, and lifestyle requirements. It's crucial to have a comprehensive eye examination and consult with an experienced surgeon. They can evaluate your specific case, discuss available options, and help you make an informed decision based on your individual needs and goals.






